O termo refração atmosférica denota os efeitos da atmosfera na geometria (curvatura) do caminho e velocidade das ondas eletromagnéticas. causada por variações no índice de refração ao longo do caminho da luz, que depende do estado físico da atmosfera. A refração terrestre denota casos em que tanto o observador quanto o alvo estão dentro da atmosfera da Terra. Se o caminho da luz viaja através da atmosfera inferior (ou seja, comumente encontrada com medições geodésicas próximas ao solo), é chamada de refração terrestre ou geodésica.
A refração terrestre é levada em consideração na balística, topografia e geodésia, radares, fotogrametria, etc.
Balística
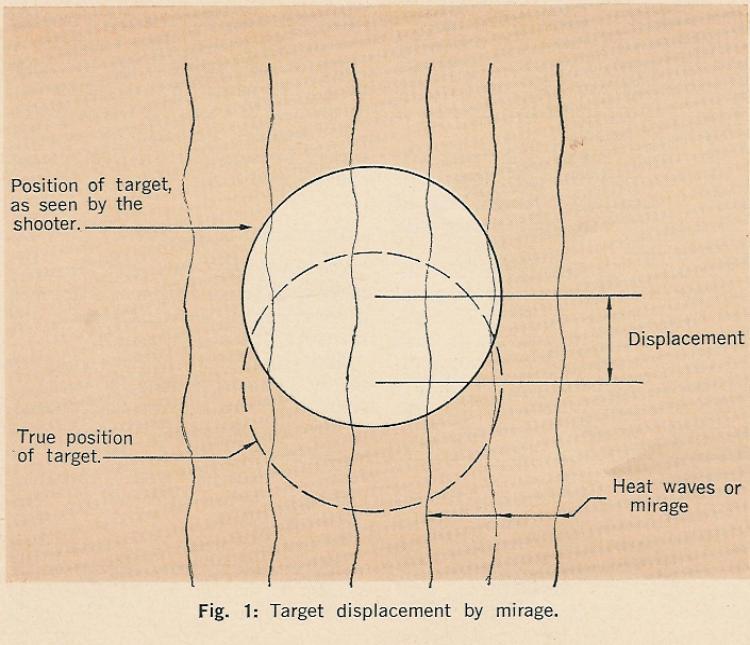
Os manuais técnicos de balística alertam para o deslocamento do alvo causado pela refração, o diagrama abaixo, extraído de um destes manuais, demonstra esta correção, onde o efeito desloca a posição aparente do alvo para cima, sendo um dos fatores que afetam a precisão do tiro.
https://sofrep.com/gear/snipers-mirage-tip-week/
Mirage and conditions that effect target image in rifle shooting
Horizonte RADAR
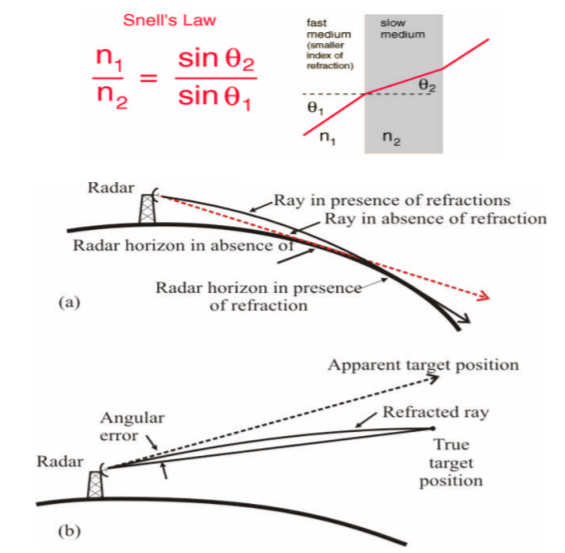
Se as ondas-radar se propagassem em linha reta, a distância ao horizonte
dependeria apenas da altura da antena, assim, sem os efeitos da refração a distância ao Horizonte RADAR seria igual à do horizonte geográfico para uma mesma elevação de antena.
O efeito da Refração normal é encurvar para baixo a trajetória das ondas-radar, acompanhando a curvatura da Terra e aumentando o Horizonte-RADAR em relação ao horizonte geográfico. excedendo o horizonte geográfico em cerca de 10% em média.
VOCAR: an experiment in variability of coastal atmospheric refractivity
Refraction Effects on EO System Detection Ranges in coastal environments
The Influence of Horizontally Variable Refractive Index Height Profile on Radio Horizon Range
System and method for using a radar to estimate and compensate for atmospheric refraction
Radar‐ray refraction associated with horizontal variations in the refractivity
Practical Method of Corrections for Refraction Errors in Arbitrary Atmosphere
Radio refractive index in the lowest 100-m layer of the troposphere in Akure, South Western Nigeria
The influence of sea surface temperature fronts on radar performance
Radar performance during propagation fades in the mid-Atlantic region
Prediction of uncertainties in atmospheric properties measured by radio occultation experiments
Effective earth radius for refraction of radio waves at altitudes above 1 km
Fotogrametria e instrumentos ópticos
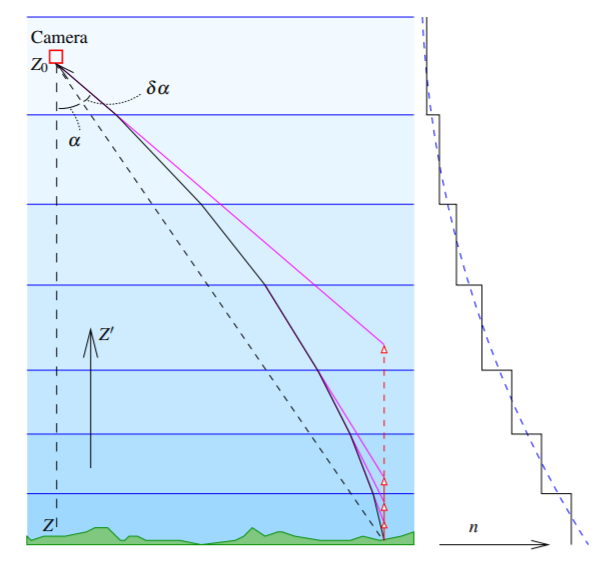
Em função dos diferentes índices de refração, os raios ópticos não são exatamente retos, sofrendo de curvaturas que levam, na imagem, ao deslocamento dos pontos de sua verdadeira posição.
Atmospheric Refraction Compensation in Terrestrial Photog rammetry
Estimation of the atmospheric refraction effect in airborne Images using radiosonde data
Correction of radar beam refraction using electro-optical measurements
Apparatus for indicating variations in the atmospheric index of refraction
Influence of atmospheric refraction on terrestrial laser scanning at long range
Differential measurement of atmospheric refraction with a telescope with double fields of view
Topografia e geodésia
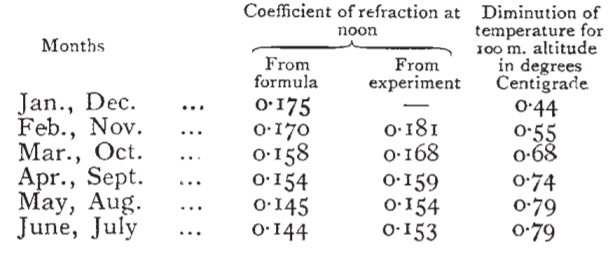
Sendo o primeiro a ajustar uma rede de triangulação pelo método de
mínimos quadrados em Brunswick, Alemanha, entre 1803 e 1807, Carl Friedrich Gauss encontrou um valor médio do coeficiente de refração k de aproximadamente +0,13. O valor gaussiano de k é bem conhecido dos topógrafos e utilizado como valor padrão da refração terrestre.
Diferentes métodos têm sido desenvolvidos para eliminar ou reduzir os efeitos da refração atmosférica nas medições geodésicas. Isso inclui o projeto de instrumentos, metodologia de observação e o uso de modelos atmosféricos com base em dados coletados na superfície da Terra.
Exemplos de observações em campo
Results of Leveling Refraction Tests by the National Geodetic Survey
An empirical investigation of atmospheric Refraction
Empirical Modelling of Refraction Error in Trigonometric Heighting Using Meteorological Parameters
The vertical temperature gradient in the lower atmosphere under daylight conditions
Experimental research on atmospheric refraction in levelling
Variation of Surface Air Temperature in Complex Terrain
Atmospheric Refraction and Its Distortion of Aerial Photographs
Temperature Stratification and Refraction Errors in Geodetic Leveling
A study of refraction in the lower Atmosphere
Empirical Method of Atmospheric Refraction Error Correction in Optical low-level Measuring
Measuring equipment for the determination of terrestrial refraction
Terrestrial Refraction and Vertical Temperature Gradient
Concepts and solutions to overcome the refraction problem in terrestrial precision measurement
Terrestrial Refraction and Vertical Temperature Gradient in the Area of Thessaloniki
Lidar and radiosonde measurements of coastal atmospheric refraction
Laboratory experiments in atmospheric optics
Atmospheric refraction of 8.7 mm radiation
Saugus‐Palmdale, California, field test for refraction error in historical leveling surveys
Atmospheric gradients from very long baseline interferometry observations
Fontes:
http://www.surveyhistory.org/carl_friedric.htm
http://fgg-web.fgg.uni-lj.si/~/mkuhar/Zalozba/Torge-Geodesy(2001).pdf
RADAR: do princípio de funcionamento à utilidade
Methods for Computing Photogrammetric Refraction Corrections for Vertical and Oblique Photographs